According to a World Bank report and data from the United States Geological Survey, Tanzania will rank third in Africa and sixth globally in projected mineral wealth by 2050.
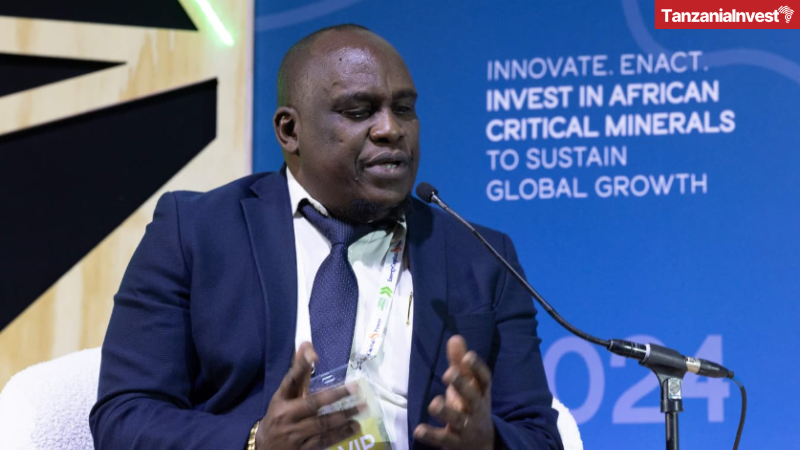
These findings were revealed on 7th November 2024, by the Managing Director of Tanzania’s State Mining Corporation (STAMICO) Vincent Mwasse at the African Critical Minerals Summit recently held in Cape Town, South Africa.
Mwasse highlighted that Tanzania is surpassed only by Mozambique and Madagascar in Africa, and globally, it ranks among the top six nations.
He added that the report highlights Tanzania’s vast deposits of graphite and other critical minerals essential for clean energy and advanced technologies.
Mwasse noted that Tanzania is uniquely endowed with a variety of minerals needed for clean energy technologies, including nickel, cobalt, lithium, rare earth elements, and niobium, underscoring the country’s competitive edge.
He highlighted: “Tanzania has begun implementing Mining Vision 2030, aimed at reducing the risk of investors incurring losses by conducting research in areas lacking geological information, thereby ‘de-risking the sector.’ The goal of this strategy is to increase mineral exploration through airborne surveys (High-Resolution Airborne Survey) from the current 16% to 50% by 2030.”
He elaborated that the effort aims to attract local and international investors while ensuring the country’s mineral wealth benefits its citizens, with the Tanzanian government committed to enhancing the value of its mineral resources through domestic processing and refining facilities. Mwasse highlighted: “For example, the Kabanga Nickel multi-metal smelter in Kahama will not only serve Tanzania but also neighboring countries like Burundi and the Democratic Republic of Congo.”
Furthermore, by investing in geological research, adopting investor-friendly policies, and fostering regional partnerships, Tanzania is charting a course for long-term prosperity and sustainable development in the mining sector.
Mwasse also stressed the importance of regional cooperation in maximizing the value of Africa’s critical minerals, andcost-benefit analyses to determine the most suitable locations for industrial investments, creating jobs and retaining more revenue within the continent.
Tanzania’s Growing Mining Potential
Tanzania is emerging as a significant player in the global mining sector, particularly for critical minerals such as cobalt, nickel, copper, and manganese.
The country is focusing on developing its mineral resources to support the growing demand for these metals, especially in the context of electric vehicle (EV) batteries and renewable energy technologies.
One of the key projects in Tanzania is the Kabanga Nickel Project, located in the north-western part of the country.
The project boasts an estimated reserve of approximately 44 million tons, with an average nickel grade of 2.61%, copper at 0.35%, and cobalt at 0.19%.