On 26th June 2023, the Tanzanian parliament approved a government budget of TZS 44.4 trillion (about USD 18.4 billion) for the 2023/2024 financial year that starts on 1st July 2023 and ends on 30th June 2024.
The Finance Act 2023 was approved by 95% of the members of parliament after a two-week debate.
The total budget for 2023-2024 has been increased by 6.9% from TZS 34.88 trillion allocated in the 2022-2023 budget.
The theme for this year’s budget as presented by the Minister of Finance of Tanzania Dr Mwigulu Nchemba is “Accelerating Economic Climate and Change Enhancing Recovery, Adaptation/Mitigation, Productive Sectors for Improved Livelihood.”
The budget includes the following macroeconomic policy targets:
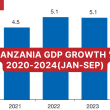
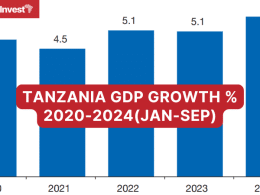
- achieving an estimated real GDP growth of 5.2% by 2023;
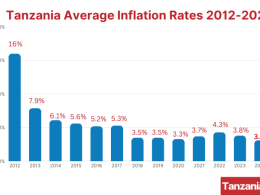
- containing inflation at a single-digit range of between 3% and 7% in the medium term;
- attaining tax revenue collection of 12% of the GDP in 2023/24;
- achieving domestic revenue collection of 14.9% of the GDP in 2023/24;
- containing budget deficit below 3% of the GDP;
- maintaining foreign reserves sufficient to cover at least four months of imports of goods and services.
Development expenditure is expected to account for 31.7% of the total budget in 2023/24. Energy and transportation infrastructure projects will drive the growth of development expenditure.
The 2023-2024 budget will be largely funded by domestic revenue which is expected to account for 70.6% of the total budget. Domestic revenue growth is expected to be driven by a 13.0% increase in tax revenue from TZS 23.2 trillion in 2022-2023 to TZS 26.7 trillion in 2023-2024.
The Tanzania Revenue Authority (TRA) is expected to collect TZS 26.73 trillion in tax revenues while non-tax revenue is expected to be TZS 4.66 trillion.
About TZS 5.44 trillion would be borrowed from domestic non-concessional sources and TZS 2.1 trillion would be borrowed from external non-concessional sources.
Priority Areas For The 2023-2024 Budget
Out of TZS 44.4 trillion, TZS 30.31 trillion (68%) are for recurrent expenditure, while TZS 14.08 trillion (32%) are for development expenditure, which includes development expenditures for various projects both in Central Government and Local Government Authorities.
Priority areas include the completion of flagship and strategic projects such as:
- continuing the construction of the Standard Gauge Railway (SGR);
- revamping Air Tanzania Company Limited (ATCL);
- continuing the construction of the Julius Nyerere Hydropower Project (2,115 MW);
- construction of Ruhudji (358 MW) and Rumakali (222 MW) hydropower plants;
- development of the liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) project;
- construction of the John Magufuli Bridge (Kigongo-Busisi);
- construction of roads and bridges;
- developing special economic zones including the strategic investment area in Bagamoyo.