Coffee
 The Coffee Industry in Tanzania
The Coffee Industry in Tanzania
Production Overview
Tanzania produces approximately 1.5 million bags of coffee annually, primarily consisting of Arabica (about 70%) and Robusta (30%). Key growing regions include:
– Arabica: Kilimanjaro, Arusha, Tanga
– Robusta: Kagera, Mwanza, Morogoro
The country has around 320,000 smallholder farmers who contribute to the majority of production alongside a smaller number of large estates. The Tanzania Coffee Board (TCB) aims to increase production to 300,000 tons by the 2025/26 season through initiatives focused on quality improvement and local consumption growth.
Export Values and Volumes
In the marketing year (MY) 2024/25, Tanzania’s coffee exports are forecast to reach 1.31 million bags (60 kg each), an increase from 1.27 million bags in MY 2023/24.
This growth is attributed to improved local supplies resulting from the rehabilitation of aging plantations.
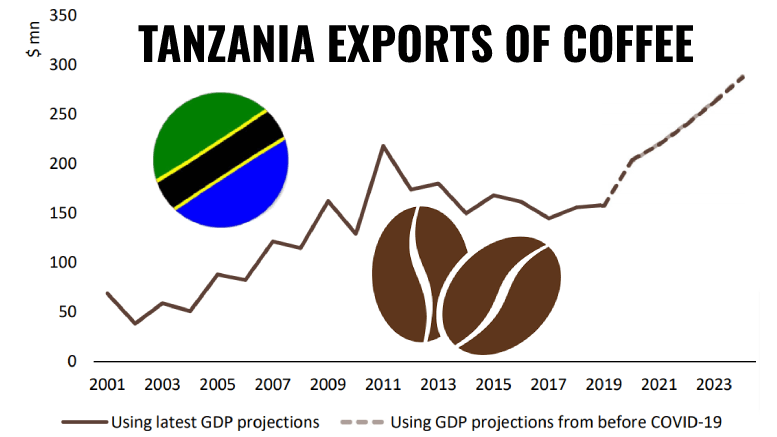
The export value of Tanzanian coffee was approximately US$ 226 million in 2022, making it the 26th largest exporter of coffee globally. In 2023, exports were valued at US$ 293.75 million, reflecting a growing demand for Tanzanian coffee on international markets.
Main Export Destinations
Tanzania’s coffee exports are primarily directed towards several key markets:
European Union: The largest destination, accounting for about 59% of total exports, with an estimated 752,000 bags in MY 2023/24.
Japan: A significant market with exports valued at approximately US$ 81.2 million in 2022.
United States: Exports reached around US$ 18.9 million, with increasing demand noted in recent years.
Other notable destinations include:
Italy: US$ 21.3 million
Germany: US$ 18.1 million
South Africa: US$ 14.7 million
Morocco and Russia also represent important markets.
The fastest-growing export markets between 2021 and 2022 included Japan (US$ 35.1 million), South Africa (US$ 11.2 million), and the United States (US$ 7.53 million).
Market Dynamics
The Tanzanian coffee market operates through various channels:
Farmgate Sales: Farmers sell directly to private buyers or cooperatives.
Direct Exports: Some farmers export directly to international buyers with registered contracts.
Online Auctions: Six government-approved auction sites facilitate competitive bidding for Tanzanian coffees.
Despite these channels, challenges remain in ensuring consistent quality and compliance with international standards.
Challenges and Opportunities
The industry faces several challenges:
Environmental Regulations: New EU regulations demand sustainable practices that do not contribute to deforestation.
Quality Control: Improving processing methods is essential for maintaining competitiveness on the global stage.
Local Consumption: Increasing domestic consumption remains a goal, as coffee is often more expensive than tea.
Future prospects hinge on strategic initiatives focused on quality enhancement and sustainable practices, alongside ongoing rehabilitation efforts that aim to stabilize Tanzania’s position in international markets.
In summary, while Tanzania’s coffee industry encounters various challenges, ongoing efforts in production rehabilitation and quality improvement position it well for future growth in an increasingly competitive global market.
Last Updated: 23rd October 2024
References:
[1]https://apps.fas.usda.gov/newgainapi/api/Report/DownloadReportByFileName?fileName=Coffee+Annual_Dar+Es+Salaam_Tanzania_TZ2024-0002.pdf
[2] https://dailycoffeenews.com/2024/07/01/tanzania-coffee-report-production-rising-as-old-farms-get-new-life/
[3] https://fas.usda.gov/data/tanzania-coffee-annual-8
[4] https://oec.world/en/profile/bilateral-product/coffee/reporter/tza
[5] https://tradingeconomics.com/tanzania/exports/coffee-tea-mate-spices