International credit ratings agency Fitch Ratings has reaffirmed Tanzania’s Long-Term Foreign-Currency Issuer Default Rating (IDR) at ‘B+’ with a Stable Outlook, as announced on 15th December 2023.
The rating reflects a detailed analysis of Tanzania’s economic and financial landscape, considering various key rating drivers.
- Credit Fundamentals: The ‘B+’ rating is underpinned by Tanzania’s relatively strong macroeconomic performance, marked by high real GDP growth, low inflation, and a moderate debt level. These factors are supported by the country’s increased reform momentum, particularly under the IMF program. However, the rating is constrained by challenges such as weak governance, inefficiencies in public financial management, including issues in revenue collection, and a weak macroeconomic policy framework that has contributed to foreign currency shortages.
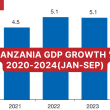
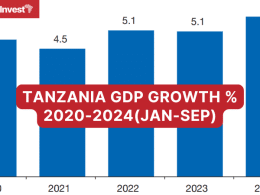
- Growth Projections: Fitch expects Tanzania’s real GDP growth to accelerate to 5.0% in 2023 and 5.5% in 2024, up from 4.7% in 2022. This growth is driven by increased activity in agriculture, mining, and tourism, along with significant infrastructure investments. The long-term growth outlook is further bolstered by the development of offshore gas fields and LNG production, which is expected to start contributing to the GDP in 2029.
- External Pressures and FX Reserves: Tanzania faces external pressures, particularly from a reduced level of FX inflows, a higher import bill, and debt amortization. These challenges have led to FX shortages and a depreciation of the Tanzanian shilling against the US dollar. The Bank of Tanzania has responded by increasing FX sales and allowing greater exchange rate flexibility. Fitch notes that FX reserves reached USD 4.9 billion at the end of September 2023, a decrease from USD 6.4 billion at the end of 2021.
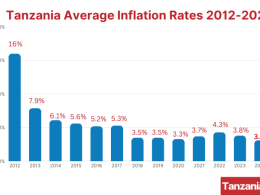
- Inflation and Monetary Policy: Inflation is projected to remain within the Bank of Tanzania’s target range of 3%-5% in 2023-2024, supported by lower food inflation and fertilizer subsidies. The transition from a monetary aggregate targeting to an interest-rate-based monetary policy framework is underway, with plans to adopt the new framework by January 2024.
- Public Financial Management: Tanzania has a history of revenue underperformance and weak cash management. The government, under the ECF program, has started implementing strategies to clear existing arrears and prevent new accumulations. This includes the verification of arrears and the issuance of special bonds.
- Fiscal Consolidation and Debt Dynamics: The government aims to reduce the fiscal deficit to 2.8% of GDP in FY24, from 4.3% in FY23. Central government debt-to-GDP is moderate at 45% in FY23, with a high share of concessional debt. Interest payments have risen, reflecting lower revenue and tight global financial conditions.
- Governance and Political Stability: The report acknowledges improvements in political stability under the current government’s reforms, including the lifting of a ban on opposition rallies and the establishment of a task force for constitutional reform. However, there have been recent arrests of some opposition members.
- ESG Governance: Tanzania’s ESG Relevance Score reflects the impact of governance indicators on the credit profile. Issues like corruption and institutional capacity weaknesses are noted, despite recent improvements in governance.
In summary, Fitch Ratings’ affirmation of Tanzania’s ‘B+’ rating with a Stable Outlook provides a nuanced view of the country’s economic strengths and challenges. It highlights Tanzania’s potential for continued growth and development, balanced against the need for ongoing reforms and policy improvements.