On 14th June 2024, Fitch Ratings affirmed Tanzania’s Long-Term Foreign-Currency Issuer Default Rating (IDR) at ‘B+’ with a Stable Outlook.
This affirmation reflects Tanzania’s robust economic growth, low inflation, and manageable government debt levels, supported by ongoing reforms under an International Monetary Fund (IMF) program. However, the rating remains constrained by governance challenges, revenue underperformance, and foreign-exchange liquidity pressures.
Key Highlights from the Fitch Report
Robust Economic Growth
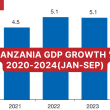
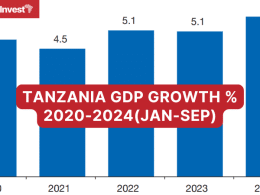
Fitch projects Tanzania’s real GDP growth to rise to 5.4% in 2024, outperforming the projected ‘B’ median of 3.5%. This growth is driven by increased activity in agriculture, mining, tourism, and substantial infrastructure investments, including flagship projects such as the Standard Gauge Railway and the Julius Nyerere Hydropower project. The economy is expected to expand further by 5.9% in 2025, bolstered by continued investments and export growth.
Strengthened Policy Framework
The Bank of Tanzania (BoT) has made significant strides in strengthening its monetary and exchange rate policy effectiveness. Key reforms include the transition to an interest-rate-based policy framework, the adoption of a new foreign exchange intervention policy, and the revision of the interbank FX Code of Conduct. These measures are expected to enhance monetary policy transmission, although challenges remain due to ongoing FX pressures.
Foreign Exchange and Inflation Dynamics
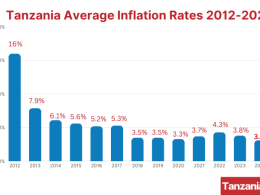
Tanzania’s gross FX reserves fell to USD 5.3 billion at the end of March 2024, from USD 5.5 billion at the end of 2023. Despite these pressures, reserves are forecasted to rise modestly to USD 5.7 billion by the end of 2025, supported by an improved trade balance, foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows, and official disbursements. Inflation is expected to decline to 3.5% in 2025, within BoT’s target range of 3-5%, driven by monetary policy tightening and lower food inflation.
Fiscal Outlook and Debt Sustainability
Fitch expects Tanzania’s budget deficit to narrow to 2.9% of GDP in the fiscal year ending June 2024, and further to 2.6% in FY25. The government’s commitment to fiscal discipline is evident through administrative efficiency gains and a rise in the central government revenue-to-GDP ratio. Government debt is projected to peak at 46% of GDP in FY24, well below the ‘B’ median of 53.2%, before declining to 44.5% in FY25.
Commitment to Clearing Arrears
The Tanzanian government is actively addressing legacy arrears and has verified outstanding claims, including those owed to the National Social Security Fund and the National Health Insurance Fund. The government plans to clear these arrears through fiscal adjustments and the issuance of special bonds by the end of FY25.
ESG Considerations
Tanzania’s Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Relevance Scores remain significant. The country has an ESG Relevance Score of ‘5’ for Political Stability and Rights, and for Rule of Law, Institutional and Regulatory Quality, and Control of Corruption. These scores reflect the substantial impact of the World Bank Governance Indicators on Tanzania’s credit profile, highlighting ongoing challenges despite recent improvements.
Future Outlook and Potential Rating Changes
Negative Rating Triggers:
- Persistent current account deficits not financed by FDI.
- Significant weakening in trend growth or fiscal consolidation efforts.
Positive Rating Triggers:
- Reduction in primary deficits due to stronger revenue mobilization.
- Enhanced transparency and confidence in the exchange rate regime.
- Proven improvements in the macroeconomic policy framework.
Fitch’s assessment underscores Tanzania’s potential for sustained economic growth and fiscal stability while acknowledging the need for continued reforms and governance improvements to enhance the country’s credit profile further.