On 2nd of October 2020, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) approved a second six-month tranche of USD 11.6 million debt service relief to Tanzania under the Catastrophe Containment and Relief Trust (CCRT).
The grant will be used to cover the debt service of Tanzania falling due to the IMF from 14th October 2020 to 13th April 2021.
Relief on debt service will free up scarce financial resources for vital emergency medical and other relief efforts to combat the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This is the second tranche of debt relief to Tanzania under the CCRT. The first tranche was approved in June 2020 to cover Tanzania’s debt service falling due from 12th June to 13th October 2020, the equivalent of USD 14.3 million.
Grant contributions under the CCRT are provided from donors from the UK, Japan, Germany, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Norway, China, Mexico, Sweden, Bulgaria, Luxembourg, and Malta.
The IMF explains: “Staff assesses that Tanzania is pursuing appropriate macroeconomic policies to address the global pandemic, although there are several risks, and more could be done to support affected sectors such as tourism and hospitality. The governance safeguards put in place, and the authorities’ use of IMF debt relief to prop-up reserves ensure that resources are appropriately used to provide emergency support to mitigate the impact of the pandemic on the economy.”
However, the IMF staff noted that Tanzania could do more to support the critical tourism and hospitality sectors.
IMF Tanzania Economic Outlook
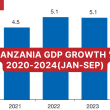
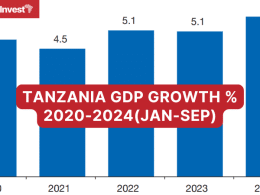
COVID-19 continues to have an adverse economic impact on Tanzania. IMF projects that the Tanzanian economy will grow by 2.8% in FY 2020/21, down from a projected 5.9% before the pandemic.
The main driver of the deceleration is the impact of lower global demand on the tourism sector, which accounts for 15% of GDP and 35% of exports.
The external shock is expected to widen the current account deficit to 5.1% of GDP, opening a financing gap of about 1% of GDP.
The fiscal impact of the pandemic is estimated at about 0.5% of GDP, mainly due to lower tax revenue collection.