The International Monetary Fund (IMF) Executive Board has concluded the fourth review of Tanzania’s Extended Credit Facility (ECF) arrangement and the first review under the Resilience and Sustainability Facility (RSF) arrangement, resulting in immediate disbursements of approximately US$ 148.6 million and US$ 55.9 million, respectively.
The ECF arrangement, approved in July 2022 for a total of SDR 795.58 million (about US$ 1,046.4 million at the time), aims to preserve macroeconomic stability, strengthen recovery, and promote sustainable and inclusive growth.
Total disbursements under the ECF now amount to US$ 754.3 million.
The RSF arrangement, approved in June 2024 with a total access of US$ 791.6 million, supports Tanzania’s climate reform agenda to address risks associated with climate change and enhance economic resilience.
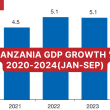
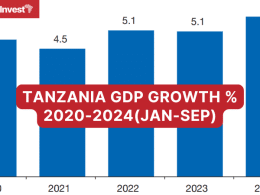
The IMF explains that Tanzania’s economy demonstrated growth momentum in 2024, with real GDP rising to 5.4% in the first half of the year compared to 5.1% in 2023.
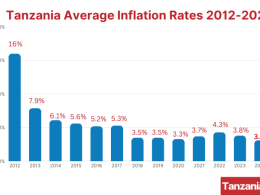
Inflation remains within the central bank’s target, supported by a narrowing current account deficit driven by robust service exports and reduced imports.
Pressures in the foreign exchange market eased due to tight monetary policy, exchange rate flexibility, and seasonal current account flows.
The Tanzanian government’s economic reform program under the ECF remained on track, meeting all quantitative performance criteria and indicative targets for June 2024. However, mixed performance on structural benchmarks led to requests for extensions on incomplete reforms to March 2025.
Growth is expected to strengthen in the medium term, contingent on the successful implementation of reforms supported by the ECF and RSF arrangements. Near-term priorities include fiscal consolidation while preserving social spending, enhancing monetary policy effectiveness, and maintaining exchange rate flexibility.
IMF’s Recommendations
Following the Board meeting, Mr. Li, IMF Deputy Managing Director and Acting Chair, emphasized the importance of Tanzania’s commitment to reforms for sustainable growth and macroeconomic stability. Key recommendations include:
- Enhancing domestic revenue mobilization and public investment efficiency.
- Addressing human capital gaps through increased social spending.
- Maintaining exchange rate flexibility to counter potential market pressures.
- Upgrading financial regulation to bolster stability and inclusion.
The IMF also highlighted the need for private sector development by simplifying regulations, enhancing governance, and implementing anti-corruption measures.
Tanzania’s ongoing climate reform agenda under the RSF is expected to attract technical and financial support, further advancing sustainable growth.
IMF Extended Credit Facility and Resilience and Sustainability Facility
The Extended Credit Facility (ECF) is the IMF’s primary tool for providing medium-term support to low-income countries, focusing on maintaining macroeconomic stability and fostering inclusive growth.
The Resilience and Sustainability Facility (RSF) is a more recent initiative by the IMF, launched in 2022 to help countries address long-term structural challenges, including those related to climate change.
In July 2022, Tanzania entered into a new ECF arrangement with the IMF, approved for total access of SDR 795.58 million (about US$1,046.4 million). This arrangement aims to support economic recovery, preserve macro-financial stability, and promote sustainable and inclusive growth.
Tanzania’s RSF arrangement, approved in June 2024, provides total access to SDR 596.7 million (about US$ 791.6 million). The RSF supports Tanzania’s ambitious climate reform agenda, focusing on improving economic resilience to climate risks while fostering sustainable development.