The World Bank Group has released its Country Climate and Development Report (CCDR) for Tanzania, revealing the urgent need for climate action to ensure resilient, inclusive, and low-carbon development.
The report warns that without decisive measures, Tanzania could face a 4% GDP decline by 2050 and identifies US$ 19 billion in funding requirements to achieve its climate commitments by 2030.
Tanzania is highly vulnerable to climate change, ranking 47th globally in susceptibility and 150th in readiness to cope.
The report indicates that inaction could push 2.6 million more people into poverty and displace 13 million through internal migration. However, proactive climate measures could significantly mitigate these risks.
Key findings from the report include risks to GDP, with potential reductions of 4% by 2050 under a dry/hot climate scenario, and the possibility of reducing climate-related economic losses by 25% through investments in adaptation.
Agriculture, the backbone of Tanzania’s economy, is particularly vulnerable, with projected declines in crop and livestock production. The country requires US$19.23 billion to meet its updated Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) commitments by 2030.
The CCDR outlines five actionable pathways to ensure Tanzania integrates climate considerations into its development plans. These include enhancing social protection and access to WASH and health services, improving land and water management to boost agricultural productivity and promote nature-based tourism, developing climate-resilient and low-carbon infrastructure such as transport and energy systems, strengthening governance and institutional frameworks for climate action, and mobilizing diverse funding mechanisms, including private investments and carbon markets.
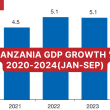
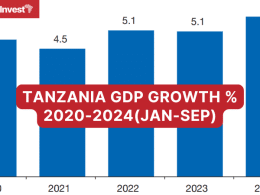
“Tanzania has made impressive social and economic progress supported by steady GDP growth since 2000, but high poverty levels and insufficient investment to transform rainfed, low-productivity agriculture leave the economy vulnerable to climate risks,” said Nathan Belete, World Bank Country Director.
“Our government appreciates that climate change presents both a challenge and an opportunity for Tanzania’s future. We are committed to investing in our people and ensuring that our most vulnerable communities are equipped to face climate challenges because we know that these measures also unlock new avenues for more sustainable growth,” said Dr. Mwigulu Nchemba, Minister of Finance.
The World Bank introduced Country Climate and Development Reports (CCDRs) to integrate climate considerations with national development. Tanzania’s CCDR aligns with Vision 2050 and updated NDCs, providing a roadmap for sustainable growth.