The World Bank (WB) has recently released its Global Economic Prospects report of January 2022, which stresses that global recovery is set to decelerate markedly amid continued Cvoid-19 flare-ups, and output in emerging market and developing economies (EMDEs) will remain substantially below the pre-pandemic trend over the forecast horizon.
The WB explains that the global outlook is clouded by various downside risks, including renewed Covid-19 outbreaks due to Omicron or new virus variants, the possibility of de-anchored inflation expectations, and financial stress in a context of record-high debt levels.
In addition, climate change may increase commodity price volatility, creating challenges for almost two-thirds of EMDEs that rely heavily on commodity exports and highlighting the need for asset diversification.
However, in his foreword, David Malpass, President of the World Bank Group, reminds that international trade has picked up, and high commodity prices are benefiting many developing countries.
Specifically, the report highlights that in agricultural commodity-exporting countries like Ethiopia, Kenya, and Tanzania, growth will be supported by increasing agricultural production encouraged by high prices of agricultural commodities (coffee, cotton), investments to raise yields, and intensification of land use.
However, the expansion of agriculture in countries like Burundi, Comoros, Madagascar, and Tanzania is likely to be constrained by various sources of uncertainty such as droughts and below-average rainfall.
Furthermore, remaining travel restrictions as well as the reintroduction of curbs on international travel to contain the spread of the Omicron variant held back the recovery of tourism to pre-pandemic levels in many Sub-Saharan economies, namely Kenya, South Africa, and Tanzania.
Against this mix of encouraging and troubling news, Malpass commented: “It is clear that challenging times lie ahead for the global economy—and particularly for developing countries—as economic stimulus slows and credit conditions tighten. Putting more countries on a favorable growth path will require concerted international action and a comprehensive set of national policy responses.”
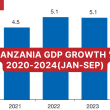
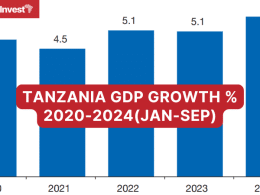
But all in all, the report keeps a positive eye on Tanzania, estimating a GDP growth of +4.8% in 2021, and forecasting a GDP growth of +5.4% and 5.9% in 2022 and 2023.