Mr. Bo Li, Deputy Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), just concluded his visit to Tanzania, expressing admiration for the country’s commitment to maintaining macroeconomic stability amidst global challenges and its dedication to an ongoing reform program.
During his visit, Mr. Li engaged with various Tanzanian officials, including Vice President Dr. Philip Isdor Mpango, Minister of Finance Dr. Mwigulu Nchemba, and Bank of Tanzania Governor Emmanuel Tutuba.
He also interacted with representatives from the private sector, civil society, and development partners.
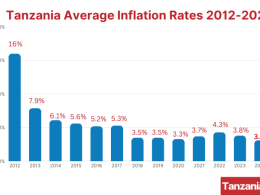
Mr. Li praised Tanzania’s swift policy response to contain inflation and safeguard the economy against global spillovers, particularly from the war in Ukraine.
He stated, “I commended the authorities’ commitment to preserving Tanzania’s macroeconomic stability in a challenging global environment. I welcomed the authorities’ continued commitment to their reform program supported by the IMF’s Extended Credit Facility (ECF) approved in July 2022.”
The reform program, as outlined by the IMF, includes creating fiscal space for social spending and high-impact public investment, enhancing monetary policy and financial supervision frameworks, strengthening governance, and advancing structural reforms.
The program aims to promote strong, sustainable, and inclusive growth.
Mr. Li also encouraged Tanzania to enhance domestic revenue mobilization through tax reforms, which will help finance social spending and priority investment. He emphasized the importance of investing in human capital through increased spending on education and health.
The IMF in Tanzania
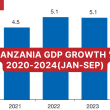
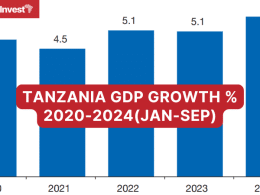
According to the IMF, Tanzania’s real GDP growth is projected to rebound to about 7% over the medium term, inflation is expected to return to the BoT’s target, and the current account deficit to moderate over the medium term as the global shocks subside and the authorities’ reforms start to pay off.
In July 2022, the Executive Board of the IMF approved a 40-month extended arrangement under the Extended Credit Facility (ECF) for Tanzania, with access equivalent to SDR 795.58 (200% of quota, equivalent to USD 1,046.4 million).
In April 2023, the Executive Board completed the first review of the Extended Credit Facility (ECF) Arrangement and the 2023 Article IV Consultation with Tanzania.
This enabled the immediate disbursement of SDR 113.37 million (about USD 153 million) for budget support, bringing Tanzania’s total access under the arrangement to about USD 304.7 million.